Comparing Vulnerability Scanners
It’s possible to run a like-for-like comparison between vulnerability scanners, but that’s not always a reliable indicator of which scanner is better. Sometimes a vulnerability scanner will come up with false positives or other issues that aren’t actually security issues at all. That’s because some scanners’stuff’ their results with ‘Informational’ issues, which aren’t really security problems at all.
It’s important to note that different vulnerability scanners are designed for different types of security needs, and they will cover different types of attack scenarios. For example, attackers may target an exposed web server or unpatched employee workstations to break into a company’s network. Different vulnerabilities require different kinds of vulnerability scanners, and these need to be considered before a business purchases one.
The cost of a vulnerability scanner depends on the features it has, as well as the number of systems it will scan. Some vulnerability scanners are cloud-based, meaning they do not require deployment or ongoing management. On the other hand, some require setting up a scanning appliance on-site, which can cost a lot of money. The additional overhead of managing a scanning appliance is not usually worth the extra cost, so it’s worth comparing price and features before committing to a vulnerability scanner.
When it comes to comparing vulnerability scanners, you should look for those with a wide range of features. Compared to pen test tools, vulnerability scanners are more convenient to use. Most of them are automated and don’t require manual intervention, which makes them easier to use for people with less experience. Some teams may hire a third-party company to run a pen test tool for them.
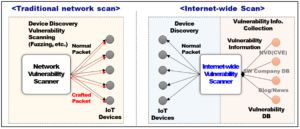
Vulnerability Scanners
While most vulnerability scanners are flexible enough to scan a variety of endpoints, the complexity of discovering mobile devices, cloud assets, and virtual machines presents a challenge. However, some scanners, such as the Tenable Nessus, offer endpoint agents that allow offline scanning and collection of results after mobile devices reconnect to the corporate network. Using this tool, users can scan mobile devices for malware. Similarly, Tripwire and Rapid7 Nexpose offer an automated workflow for categorization of devices.
Lastly, vulnerability scanners differ in how they detect vulnerabilities. For example, a discovery vulnerability scan will triage a network, rather than looking for every possible exploit. These scans will help you identify vulnerable devices and develop a game plan for a full scan. These scanners can also help you decide which vulnerabilities to address first.
Vulnerability scanners are essential tools in the cyber security arsenal. A properly-designed tool will help you identify and address the most significant technical weaknesses in your organization. It will also provide insights into the latest threats and regulations. You must also choose a tool that fits into your existing cybersecurity program. You don’t want to use a vulnerability scanner that doesn’t match your needs.
While vulnerability scanners provide a snapshot of risk at a particular point in time, they can’t offer you a comprehensive picture of your attack surface. Using a vulnerability scanner can be invaluable, but they aren’t a perfect substitute for a human expert.


