flex PCBs
Unlike rigid PCBs, which have to fit inside the end device they connect to, flexible circuit boards can be folded and bent to fit into the shape of the device. They also offer a number of other benefits, including their ability to withstand harsh environments. These factors make flex PCBs ideal for foldable electronic devices like fitness trackers, smart watches, and medical equipment.
The flexibility of a flex PCB is determined by its substrate, which is typically made of polyester or polyimide. These materials are incredibly thin, which gives the circuit board its flexibility. The copper traces that are etched on the substrate must be very small and spaced close together to maintain the flexibility of the circuit. The traces are held in place with a coverlay, which is usually made of an adhesive polyimide material. This helps protect the traces from damage and other environmental concerns, such as humidity.
In addition to thickness, the number of layers on a flex pcb is another important factor in its flexibility. The more layers a flex PCB has, the less flexible it will be. It’s best to consult with a PCB design and layout expert early in the process to decide how many layers you need for your specific project. Adding more layers will increase the price of a flex PCB, so it’s a good idea to try and reduce the number of layers wherever possible. It’s also a good idea to minimize the amount of plated through holes (vias) on your flex PCB, as they can add to its cost and may not provide enough space for all of your connections.
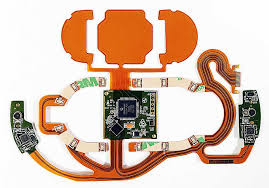
Can flex PCBs be used in foldable electronic devices?
Another aspect that determines the flexibility of a flex PCB is its bend ratio. This is calculated as the bend radius divided by the PCB thickness. The higher the bending ratio, the less flexible a flex PCB will be. It’s best to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines when determining the best bend ratio for your flex PCB. Regular bending and flexing can subject Flex PCBs to mechanical stress that can lead to permanent damage. To avoid this, meticulous design and careful material selection are critical.
For example, a flex PCB with frequent bending will require a high-bend-ratio to prevent the copper traces from breaking or becoming damaged. It is also a good idea to use an adhesive polyimide to strengthen the flex PCB in areas that are susceptible to vibrations or other mechanical stress.
Another common concern with flex PCBs is the potential for moisture or chemical exposure to damage or warp them. To address this, a flex PCB must be designed with appropriate tolerances and features, including the use of a thermal pad. In addition, the flex PCB must be designed with reference plane layers and shielding to control impedances and signal integrity. For further protection, the flex circuit should include stiffeners to prevent it from being pulled or lifted during assembly and operation. The stiffeners can be applied to plated through holes or vias, and they should be placed near the area that will experience the most mechanical stress.


